 I was continuing discussion on Richard Carrier vs. the Apologists but the format of the blog posting system made a detailed conversation difficult, so I decided to continue here. My core argument is that the premises of Kalam are incoherent. I also think some of the responses are as well.
I was continuing discussion on Richard Carrier vs. the Apologists but the format of the blog posting system made a detailed conversation difficult, so I decided to continue here. My core argument is that the premises of Kalam are incoherent. I also think some of the responses are as well.
But what do we mean by incoherent?
Richard interpreted that to mean logically impossible, but my intent was that incoherence is a property of the semantics of the words. Statements are incoherent when they don’t make sense or only make sense with a very narrow and unwarranted reading of the statement. The following argument follows a fairly standard analytic tradition analysis of examining the meaning of statements. I am currently fond of David Lewis’s school of thought on semantics, where the meaning of words exist as a combination of mild referential attachment, coherence within a network of other words, and, importantly, some words within that network achieve what is called “reference magnetism” in that they are tied to reality in significant ways and pull at the meaning of other words.
For instance, consider Premise 1 of a modern take on Kalam:
All things that begin to exist have a cause.
OK, so what does begin to exist mean? And how about cause? Let’s unpack “begin to exist,” first. We might say in our everyday world of people that, say, cars begin to exist at some point. But when is that point? For instance, is it latent in the design for the car? Is it when the body panels are attached on the assembly line? Is it when the final system is capable of car behavior? That is, when all the parts that were in fact designed are fully operational?… Read the rest



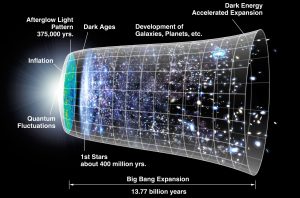
 The simulation hypothesis is perhaps a bit more interesting than how to add clusters of neural network nodes to do a simple reference resolution task, but it is also less testable. This is the nature of big questions since they would otherwise have been resolved by now. Nevertheless, some theory and experimental analysis has been undertaken for the question of whether or not we are living in a simulation, all based on an assumption that the strangeness of quantum and relativistic realities might be a result of limited computing power in the grand simulator machine. For instance, in a virtual reality game, only the walls that you, as a player, can see need to be calculated and rendered. The other walls that are out of sight exist only as a virtual map in the computer’s memory or persisted to longer-term storage. Likewise, the behavior of virtual microscopic phenomena need not be calculated insofar as the macroscopic results can be rendered, like the fire patterns in a virtual torch.
The simulation hypothesis is perhaps a bit more interesting than how to add clusters of neural network nodes to do a simple reference resolution task, but it is also less testable. This is the nature of big questions since they would otherwise have been resolved by now. Nevertheless, some theory and experimental analysis has been undertaken for the question of whether or not we are living in a simulation, all based on an assumption that the strangeness of quantum and relativistic realities might be a result of limited computing power in the grand simulator machine. For instance, in a virtual reality game, only the walls that you, as a player, can see need to be calculated and rendered. The other walls that are out of sight exist only as a virtual map in the computer’s memory or persisted to longer-term storage. Likewise, the behavior of virtual microscopic phenomena need not be calculated insofar as the macroscopic results can be rendered, like the fire patterns in a virtual torch.