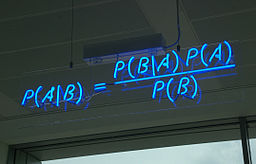While reviewing reporting on the RNC this afternoon, I found myself curious about the protocols at news organizations with respect to their editorial boards. For instance, does the Washington Post editorial board require that claimed facts within all opinion pieces are not clearly disputed? Does the New York Times? I suspect yes, which is what we see in the lawsuit filed by Sarah Palin against the New York Times concerning the suggestion that Palin’s campaign was relevant to the shooting of Gabby Giffords. There was at least a debate that rose to the level of the Opinion Editor, if not the board.
While reviewing reporting on the RNC this afternoon, I found myself curious about the protocols at news organizations with respect to their editorial boards. For instance, does the Washington Post editorial board require that claimed facts within all opinion pieces are not clearly disputed? Does the New York Times? I suspect yes, which is what we see in the lawsuit filed by Sarah Palin against the New York Times concerning the suggestion that Palin’s campaign was relevant to the shooting of Gabby Giffords. There was at least a debate that rose to the level of the Opinion Editor, if not the board.
I was investigating this because I am curious how WaPo handles Trumpy columnists like Mark Thiessen and Hugh Hewitt, who are mostly cheerleaders without baggage for the current president, with only occasional whataboutisms and other distracting suggestions about Biden’s candidacy. They don’t defend lies and cons. They just cheer. Meanwhile, the board itself came down hard on the repeated falsehoods of Pamela Bondi and the ongoing slaughter of truth in the service of the Trump 2020 campaign.
The mainstream press represents Trump and cronies as conmen and women, manipulative, self-serving, corrupt, cruel, ignorant, ineffectual, morally questionable, and out-and-out liars. And the press uses facts to do so. Yet Trump maintains a remarkable following despite this evidence, with many quizzical onlookers at a loss as to the psychology of Trump’s followers.
In this modern example, there are many, many resources that can be used to fact check and form opinions. Yet people choose to rely on only a few and discount others as being biased.
I was recently reading some fairly detailed Bayesian analysis by philosophers concerning Hume’s argument against miracles.… Read the rest