The unalloyed stupidity of reckless tariffing and threats by the Trump administration against trading partners and allies around the world is baffling and deeply concerning. Even when a serious economist admits that tariffs can play a role in helping onshore manufacturing, they also slam the uncertainty that Trump’s mercurial behavior imposes on the world economy. Then there is the childish lashing out at universities, law firms, and perceived enemies like the former director of the US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency who contradicted Trump in 2020 on election fraud. Next we have the cruelty of rapid and wrong deportations and visa revocations based on alleged allegiances; freedom is no longer guaranteed for visitors and guests in our country. And then there are the oxymoronic efforts at efficiency in governance that involve no efforts whatsoever to identify how exactly to make our government more efficient.
This is the banality of narcissism aided by incompetence.
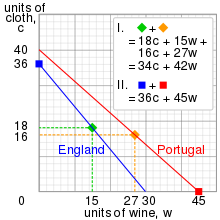
But, mercifully, the counter-currents that are pushing the country away from an economic catastrophe demonstrate the self-correcting nature of complex systems. The term “cybernetics” comes from the Ancient Greek term for the steersman of a boat. It was used by the French polymath Ampère in a volume dedicated to the structure of human knowledge where it referred to the science of governance. Ah, the Age of Enlightenment, when some hoped that through careful thought ideas like economics, government, and international relations could be improved. If only David Ricardo were here today to discuss his theory of comparative advantage with America’s leadership. Governance was in mind when Norbert Wiener invented the theory of cybernetics as a mathematical approach to system control where feedback signals steer the system towards stable patterns of operation.… Read the rest