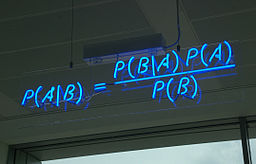The ever-present Tom Davenport weighs in in the Harvard Business Review on the topic of artificial intelligence (AI) and its impact on knowledge workers of the future. The theme is intelligence augmentation (IA) where knowledge workers improve their productivity and create new business opportunities using technology. And those new opportunities don’t displace others, per se, but introduce new efficiencies. This was also captured in the New York Times in a round-up of the role of talent and service marketplaces that reduce the costs of acquiring skills and services, creating more efficient and disintermediating sources of friction in economic interactions.
The ever-present Tom Davenport weighs in in the Harvard Business Review on the topic of artificial intelligence (AI) and its impact on knowledge workers of the future. The theme is intelligence augmentation (IA) where knowledge workers improve their productivity and create new business opportunities using technology. And those new opportunities don’t displace others, per se, but introduce new efficiencies. This was also captured in the New York Times in a round-up of the role of talent and service marketplaces that reduce the costs of acquiring skills and services, creating more efficient and disintermediating sources of friction in economic interactions.
I’ve noticed the proliferation of services for connecting home improvement contractors to customers lately, and have benefited from them in several renovation/construction projects I have ongoing. Meanwhile, Amazon Prime has absorbed an increasingly large portion of our shopping, even cutting out Whole Foods runs, with often next day deliveries. Between pricing transparency and removing barriers (delivery costs, long delays, searching for reliable contractors), the economic impacts might be large enough to be considered a revolution, though perhaps a consumer revolution rather than a worker productivity one.
Here’s the concluding paragraph from an IEEE article I just wrote that will appear in the San Francisco Chronicle in the near future:
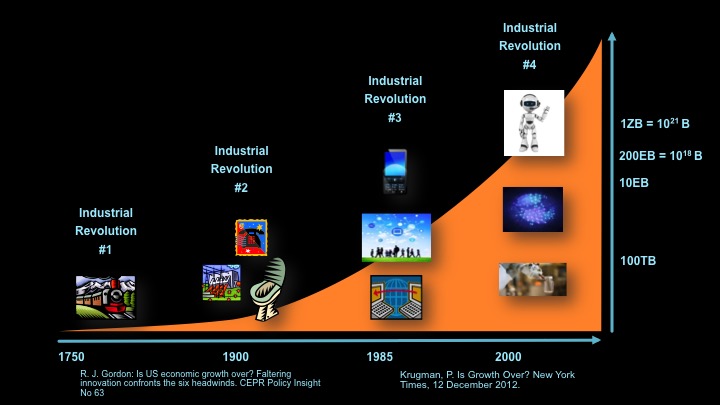
… Read the restOne of the most interesting risks also carries with it the potential for enhanced reward. Don’t they always? That is, some economists see economic productivity largely stabilizing if not stagnating. Industrial revolutions driven by steam engines, electrification, telephony, and even connected computing led to radical reshaping our economy in the past and leaps in the productivity of workers, but there is no clear candidate for those kinds of changes in the near future.